虚拟滚动(Virtual Scrolling 或 Windowing)是一种优化长列表或大数据量渲染性能的技术。它通过只渲染可视区域内的元素,避免渲染整个列表,从而大幅提升性能,减少浏览器内存消耗,提升页面流畅度。
在前端的实际开发过程中,或多或少都会遇到列表渲染优化的问题。
当数据量达到一定程度,超多的DOM结构变动就可能带来页面的内存增长,从而出现页面卡顿。
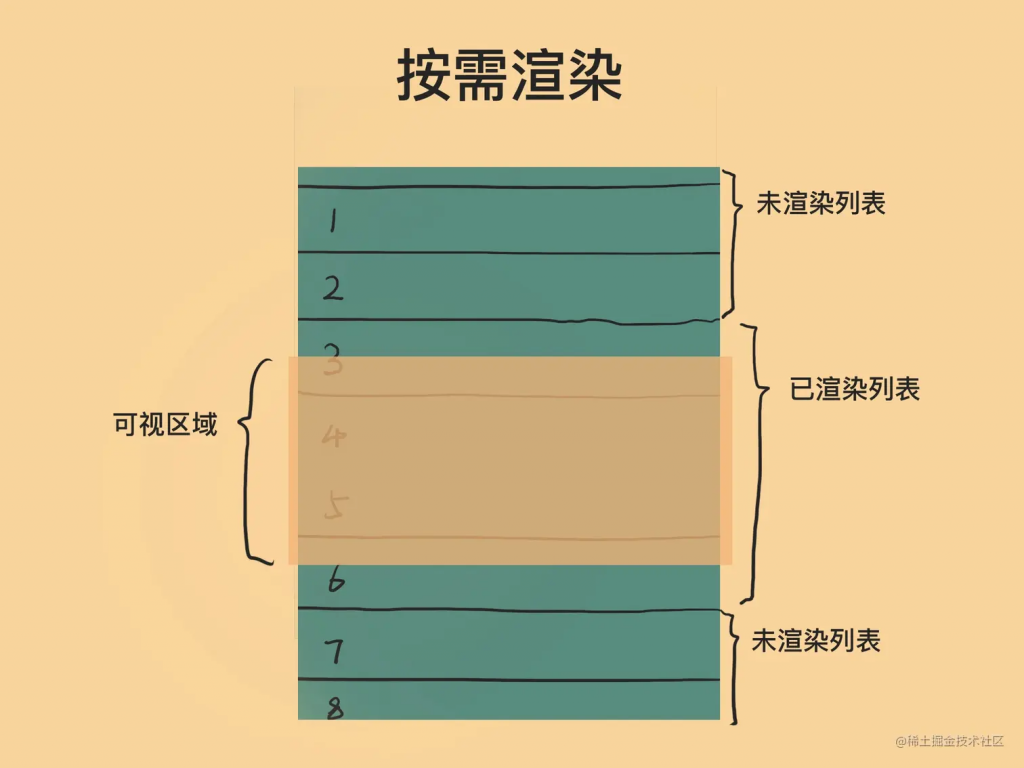
一、虚拟滚动的核心思想
现实场景中,长列表(如 10000 条记录)如果全部渲染,每一个 DOM 节点都会消耗浏览器资源。浏览器一次性渲染这么多节点:
- 首屏加载变慢;
- 滚动时卡顿严重;
- 移动设备性能更差。
而虚拟滚动的做法是:
只渲染出现在用户视窗内的部分列表项,随着滚动动态替换内容。
可以理解为:一个“窗户”只显示有限内容,其他的内容虽然在列表逻辑上存在,但在 DOM 中并不存在。
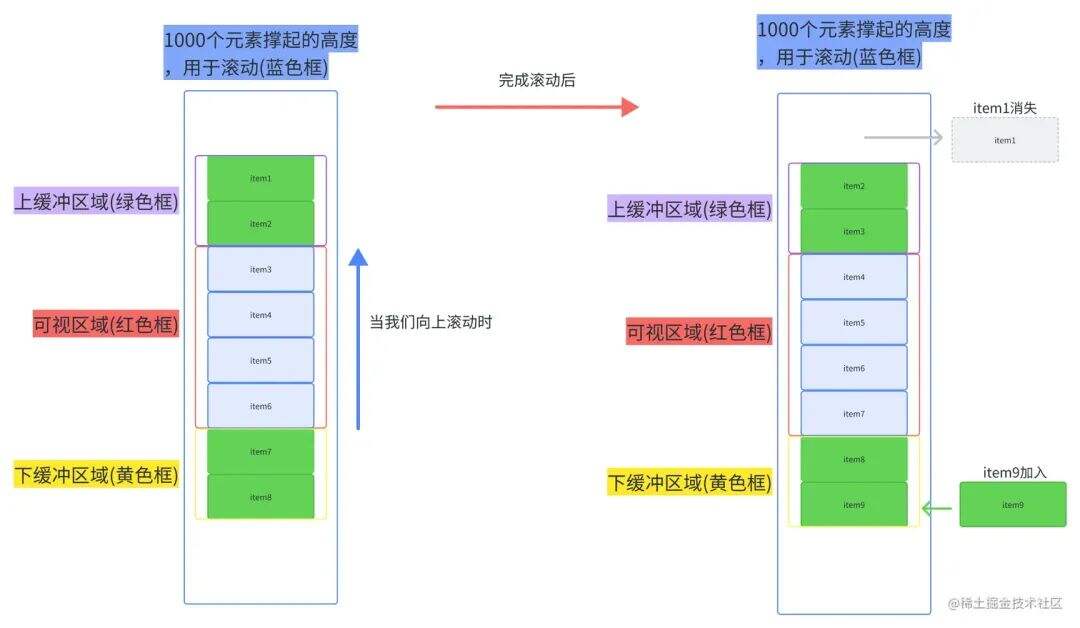
二、虚拟滚动的结构示意
假设你有一个高达 10000 项的列表,每项高度为 30px,总高度为 300,000px。
虚拟滚动通常会包含以下结构:
<div class="scroll-container" style="height: 300px; overflow-y: auto;"><br> <div class="placeholder" style="height: 300000px; position: relative;"><br> <!-- 只渲染部分 --><br> <div<br> v-for="item in visibleItems"<br> :style="{ top: item.virtualTop + 'px', position: 'absolute' }"<br> ><br> {{ item.content }}<br> </div><br> </div><br></div><br>其中:
.scroll-container: 可滚动区域,视口高度固定。.placeholder: 用于撑起整体高度,保持滚动条一致。visibleItems: 只包含当前出现在视窗附近的部分数据项。top: 根据滚动位置计算的偏移量,确保视觉位置正确。
三、虚拟滚动的关键计算
1. 可视区域高度
假设滚动容器高度为 300px,每项高度为 30px,可见数量约为 10 项。
我们会多加载几项(上下 buffer),比如 10 + 4 项,以避免滚动白屏。
2. 滚动偏移量
监听 scrollTop 值,计算出当前是从哪一项开始:
ts复制编辑startIndex = Math.floor(scrollTop / itemHeight)
endIndex = startIndex + visibleCount
visibleItems = fullList.slice(startIndex, endIndex)
3. 偏移定位
每个渲染项都加上对应的 top = itemHeight * index,通过绝对定位实现滚动感。
四、实现示范
<template>
<div
class="virtual-scroll-container"
ref="containerRef"
@scroll="handleScroll"
:style="{ height: containerHeight + 'px', overflowY: 'auto', position: 'relative' }"
>
<!-- 占位容器,撑起总高度 -->
<div :style="{ height: totalHeight + 'px', position: 'relative' }">
<!-- 仅渲染可见 + buffer 的元素 -->
<div
v-for="(item, i) in visibleItems"
:key="itemKey(item, startIndex + i)"
:style="{
position: 'absolute',
top: (startIndex + i) * itemHeight + 'px',
height: itemHeight + 'px',
boxSizing: 'border-box',
width: '100%',
padding: '0 10px',
display: 'flex',
alignItems: 'center',
borderBottom: '1px solid #eee',
backgroundColor: (startIndex + i) % 2 === 0 ? '#f9f9f9' : '#fff'
}"
>
{{ itemRender(item, startIndex + i) }}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, computed, onMounted } from 'vue'
// === Props ===
defineProps({
items: {
type: Array,
required: true,
},
itemHeight: {
type: Number,
default: 30,
},
containerHeight: {
type: Number,
default: 300,
},
buffer: {
type: Number,
default: 5,
},
itemRender: {
type: Function,
default: (_, i) => `Item ${i + 1}`,
},
itemKey: {
type: Function,
default: (_, i) => i,
},
})
// === States ===
const containerRef = ref(null)
const scrollTop = ref(0)
// === Computed values ===
const totalHeight = computed(() => props.items.length * props.itemHeight)
const visibleCount = computed(() =>
Math.ceil(props.containerHeight / props.itemHeight) + props.buffer
)
const startIndex = computed(() =>
Math.max(0, Math.floor(scrollTop.value / props.itemHeight) - props.buffer)
)
const endIndex = computed(() =>
Math.min(start
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)了解 Hana - 探索有趣的世界 的更多信息
订阅后即可通过电子邮件收到最新文章。


暂无评论